Interface란
- 일반적으로 변수, 함수, 클래스에 타입 체크를 위해 사용
- 직접 인스턴스를 생성할 수 없고 모든 메서드가 추상 메서드이다.
- 추상 클래스의 추상 메서드와 달리 abstract 키워드는 사용할 수 없다.
- ES6는 인터페이스를 지원하지 않지만 TypeScript는 지원한다
사용 이유
- 타입의 이름을 짓고 코드 안의 계약을 정의한다.
- 프로젝트 외부에서 사용하는 코드의 계약을 정의하는 강력한 방법이다.
- 다음과 같은 범주에 대해 계약(인터페이스에서 정의된 속성과 메서드)을 정의할 수 있다,
- 객체의 스펙(속성과 속성의 타입)
- 함수의 파라미터
- 함수의 스펙(파라미터,반환 타입 등)
- 배열과 객체에 접근하는 방식
- 클래스
function sayName(obj:{name: string}) {
console.log(obj.name);
}
let person = {name: june};
sayName(person);
//아래와 같이 interface사용
interface Person {
name:string
}
function sayName(obj:Person) {
console.log(obj.name);
}
let person = {name:"june"};
sayName(person);Interface를 추가하여 함수 매개변수 프로퍼티를 정의할 수 있다.
정의한 프로퍼티 값을 누락하거나 정의하지 않는 값을 인수로 전달 시 컴파일 에러가 발생한다.
Properties
- 컴파일러는 프로퍼티의 두 가지 요소를 검사한다.
- 필수요소 프로퍼티의 유무
- 프로퍼티 타입
- 아래 예약어로 프로퍼티를 세밀하게 컨트롤 할 수 있다.
- ?(Optional Propertioes)
- readonly(Readonly properties)
Optional Properties
- 프로퍼티 선언 시 이름 끝에 ?를 붙여서 표시한다.
- 인터페이스에 속하지 않는 프로퍼티의 사용을 방지하면서, 사용 가능한 프로퍼티를 기술할 때 사용한다.
- 객체 안의 몇 개의 프로퍼티만 채워 함수에 전달하는 "option bags"같은 패턴에 유용하다.
interface SquareConfig {
color?: string
width?: number
}
function createSquare(config: SquareConfig): { color: string, area: number } {
let newSquare = {color : "white", area: 100};
if (config.color) {
newSquare.color = config.color;
}
if(config.width) {
newSquare.area = config.width * config.width;
}
return newSquare;
}
let mySquare = createSquare({ color: "black" });Readonly properties
- 객체가 처음 생성될 때만 값 설정이 가능, 이 후 수정이 불가하다
- 프로퍼티 이름 앞에 readonly를 붙여서 사용한다.
readonly vs const
- readonly와 const의 공통점 : 생성 후에 배열을 변경하지 않음을 보장한다.
- 변수는 const를 사용하고 프로퍼티는 readonly를 사용한다.
const arr : number[] = [1,2,3,4];
const readonly_arr: readOnlyArray<number> =arr;
readOnly_arr[0]=12; //Error
readOnly_arr.push(5); //Error
readOnly_arr.length= 100; //Errorinterface types
- TypeScript에서 인터페이스는 함수, 클래스에서 사용할 수 있다.
- 함수
- JavaScript 객체가 가질 수 있는 넓은 범위의 형태를 기술한다.
- 프로퍼티로 객체를 기술하는 것 외에도, 인터페이스는 함수 타입을 설명한다.
- 클래스
- 클래스가 특정 통신 프로토콜을 충족하도록 명시적으로 강제한다.
function type
- 함수의 인자의 타입과 반환 값의 타입을 정의한다.
- 함수의 타입을 정의할 때에도 사용한다.
interface SearchFunc {
(source: string, subString: string): boolean
}
//변수로 직접 함수 값이 할당되었기 때문에 인수 타입 생략 가능
//TypeScript의 문맥상 타이핑 (contextual typing)이 인수 타입 추론
let mySearch: SearchFunc
mySearch = function(src,sub) {
let result = src.search(sub);
return result > -1;
}
//error: Type '(src:string, sub"string) => string` is not assignable to type 'SearchFunc'.
//Type 'string' is not assignable to type 'boolean'.
mySearch = function (src.sub) {
let result = src.search(sub);
return "string";
}class type
- 클래스가 특정 계약(contract)을 충족하도록 명시적으로 강제한다.
interface Animal {
makeSound(): void
}
class Dog implements Animal {
makeSound(): void {
console.log("멍멍");
}
interface 확장
- 클래스와 마찬가지로 인터페이스도 인터페이스 간의 확장이 가능하다.
interface Animal {
makeSound(): void
}
interface Dog extends Animal {
speed: number
}
class Bulldog implments Dog {
makeSound(): void{
console.log("멍멍");
}
}hybrid type
- 자바스크립트의 유연하고 동적인 타입 특성에 따라 인터페이스 역시 여러 가지 타입을 조합할 수 있다.
- 아래 코드와 같이, 함수 타입이면서 객체 타입을 정의할 수 있는 인터페이스도 구현할 수 있다.
interface Counter {
(start:number): string
interval: number
reset(): void
}
function getCounter(): Counter {
let counter= function (start:number) {} as Counter
counter.interval = 123;
counter.reset = function() {}
return counter;
}
let c = getCounter();
c(10);
c.reset();
c.interval = 5.0;
interface를 활용한 디자인 패턴(Strategy pattern)
- 갹체가 할 수 있는 행위들을 전략(startegy)으로 만들어 두고, 동적으로 행위의 수정이 필요한 경우 전략을 바꾸는 것만으로 수정이 가능하도록 만든 패턴이다.
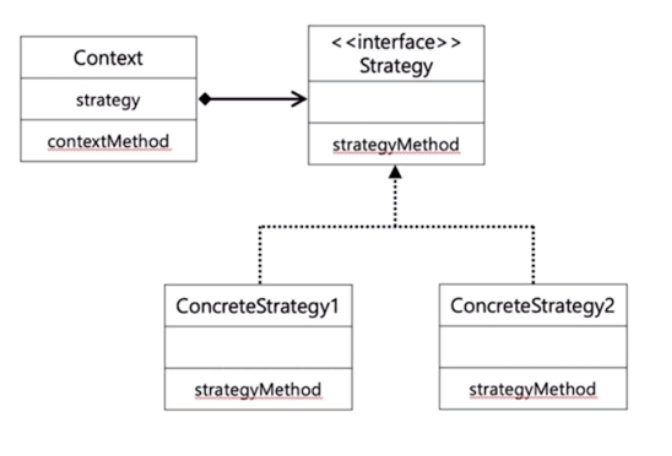
활용 사례
- 자판기 결제 방법을 현금 결제에서 카드 결제로 변경할 때, Pay 메서드 구현 변경이 필요하다.
- 메서드 수정 방식의 문제점
- OCP를 위배한다(OOP 설계 원칙)
- 시스템이 커져서 확장 될 경우 연동되는 시스템에도 영향을 줄 수 있다.
- 디자인 패턴으로 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
interface PaymentStrategy {
pay(): void
}
class CardPaymentStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
pay(): void {
console.log("Card pay!");
}
}
class CashPaymentStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
pay(): void {
console.log("Cash pay!");
}
}
class VendingMachine {
private paymentStrategy: PaymentStrategy
setPaymentStrategy(paymentStrategy: PaymentStrategy) {
this.paymentStrategy = PaymentStrategy;
}
pay() {
this.paymentStrategy.pay();
}
}
const vendingMachine = new VendingMachine();
vendingMachine.setPaymentStrategy(new CashPaymentStrategy());
vendingMachine.pay() // cash pay
vendingMachine.setPaymentStrategy(new CardPaymentStrategy());
vendingMachine.pay() // card pay
'Elice' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [TIL]6주차 1일 - Express.js (0) | 2023.09.11 |
|---|---|
| [TIL]엘리스트랙 6주차 1일 node.js (0) | 2023.09.11 |
| [TIL]엘리스트랙 5주차 3일 TypeScript (0) | 2023.09.06 |
| [TIL]엘리스트랙 5주차 1일 Node.js (0) | 2023.09.05 |
| [TIL]엘리스트랙 4주차 3일 (0) | 2023.08.30 |


